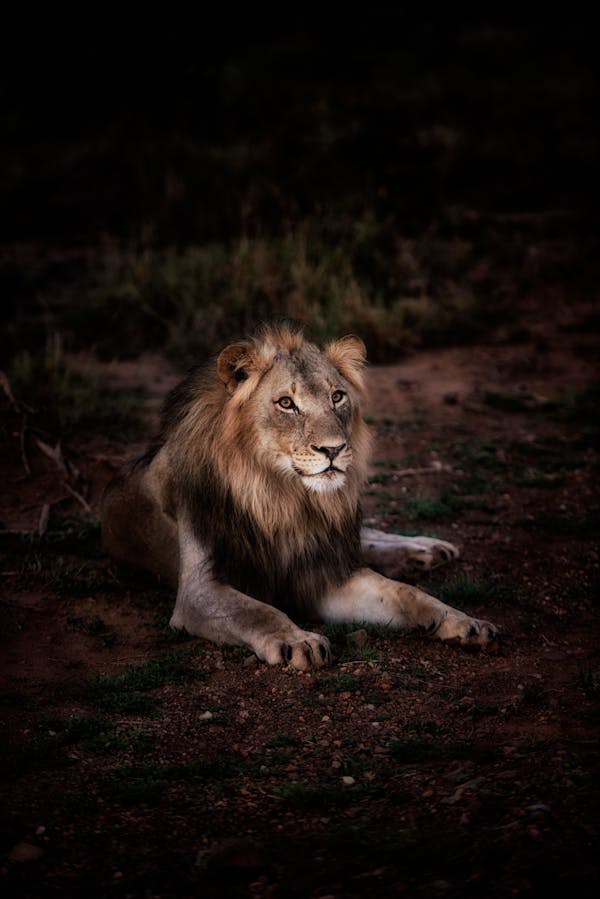
Lions are majestic and iconic big cats known for their strength, social behavior, and distinctive appearance. Here’s an overview of these fascinating creatures:
- Appearance:
- Males: Lions are unique among big cats for their prominent manes. The mane, which can vary in color from light tan to dark brown, is a distinguishing feature of male lions. It serves both to protect the neck during fights and to make the lion appear more formidable.
- Females: Lionesses do not have manes. They have a more streamlined appearance and are generally more agile and stealthy.
- Habitat: Lions are native to Africa, with the majority living in savannas, grasslands, and open woodlands. A small population of Asiatic lions also exists in the Gir Forest of India. They prefer habitats with access to water and ample prey.
- Social Structure:
- Pride: Lions are the only truly social big cats and live in groups called prides. A pride typically consists of related females, their cubs, and a few adult males. The pride structure allows for cooperative hunting and protection of territory.
- Roles: Within a pride, lionesses are the primary hunters and caregivers, while males are responsible for defending the pride’s territory from intruders.
- Diet: Lions are apex predators and primarily hunt large herbivores such as wildebeest, zebras, and buffalo. They may also scavenge or steal kills from other predators. Lions hunt cooperatively, with lionesses working together to bring down prey.
- Reproduction:
- Breeding: Lions breed year-round, with females typically giving birth to a litter of 2-4 cubs. Cubs are born blind and rely on their mothers for care and protection.
- Cub Rearing: Lionesses often give birth in secluded areas to protect the cubs from predators. Cubs are nursed for about 6 months and start eating solid food around 3 months of age. They remain dependent on their mothers for up to 2 years.
- Behavior:
- Roaring: Lions are known for their powerful roars, which can be heard from several miles away. Roaring serves to communicate with pride members, assert territory, and deter rival lions.
- Resting: Lions are known for their sedentary lifestyle. They spend a significant portion of the day resting and sleeping, conserving energy for hunting and other activities.
- Conservation Status:
- Threats: Lions face several threats, including habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and poaching. Their populations have declined significantly in recent decades due to these pressures.
- Efforts: Conservation efforts are focused on habitat protection, anti-poaching measures, and community education to reduce conflicts between lions and humans. Various organizations work to preserve and restore lion populations and their habitats.
- Cultural Significance: Lions have been symbols of power, courage, and royalty in many cultures throughout history. They are often featured in art, mythology, and heraldry, reflecting their status as the “king of the beasts.”